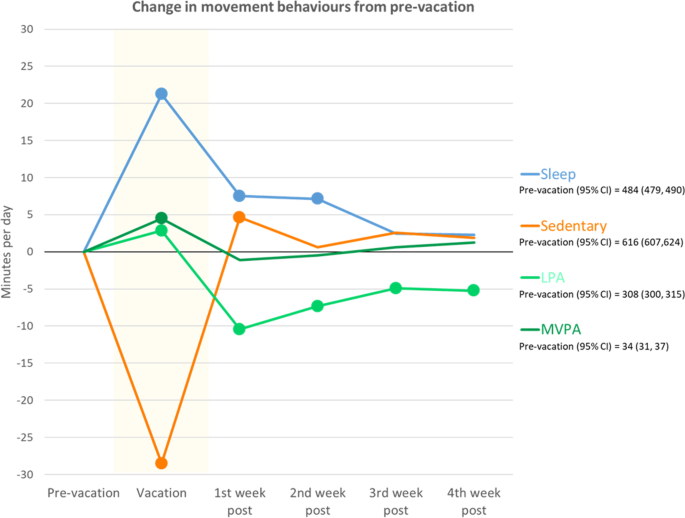
For adults, vacations represent a break from daily responsibilities of work – offering the opportunity to re-distribute time between sleep, sedentary behaviour, light physical activity (LPA) and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) across the 24-h day. To date, there has been minimal research into how activity behaviour patterns change on vacation, and whether any changes linger after the vacation. This study examined how daily movement behaviours change from before, to during and after vacations, and whether these varied based on the type of vacation and vacation duration. Data collected during the Annual Rhythms In Adults’ lifestyle and health (ARIA) study were used. 308 adults (mean age 40.4 years, SD 5.6) wore Fitbit Charge 3 fitness trackers 24 h a day for 13 months. Minute-by-minute movement behaviour data were aggregated into daily totals. Multi-level mixed-effects linear regressions were used to compare movement behaviours during and post-vacation (4 weeks) to pre-vacation levels (14 days), and to examine the associations with vacation type and duration. Participants took an average of 2.6 (SD = 1.7) vacations of 12 (SD = 14) days’ (N = 9778 days) duration. The most common vacation type was outdoor recreation (35%) followed by family/social events (31%), rest (17%) and non-leisure (17%). Daily sleep, LPA and MVPA all increased (+ 21 min [95% CI = 19,24] p < 0.001, + 3 min [95% CI = 0.4,5] p < 0.02, and + 5 min [95% CI = 3,6] p < 0.001 respectively) and sedentary behaviour decreased (-29 min [95% CI = -32,-25] p < 0.001) during vacation. Post-vacation, sleep remained elevated for two weeks; MVPA returned to pre-vacation levels; and LPA and sedentary behaviour over-corrected, with LPA significantly lower for 4 weeks, and sedentary behaviour significantly higher for one week. The largest changes were seen for “rest” and “outdoor” vacations. The magnitude of changes was smallest for short vacations (< 3 days). Vacations are associated with favourable changes in daily movement behaviours. These data provide preliminary evidence of the health benefits of vacations. The study was prospectively registered on the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trial Registry (Trial ID: ACTRN12619001430123).

Association between 24-hour movement behaviors and health-related quality of life in children

Exploring the impact of COVID-19 on the movement behaviors of children and youth: A scoping review of evidence after the first year - ScienceDirect

How Your Menstrual Cycle Affects Your Behavior
What Happens When You Sleep: The Science of Sleep

研究显示,周末休3天,更有利于健康- 医疗健康专区- 生物谷
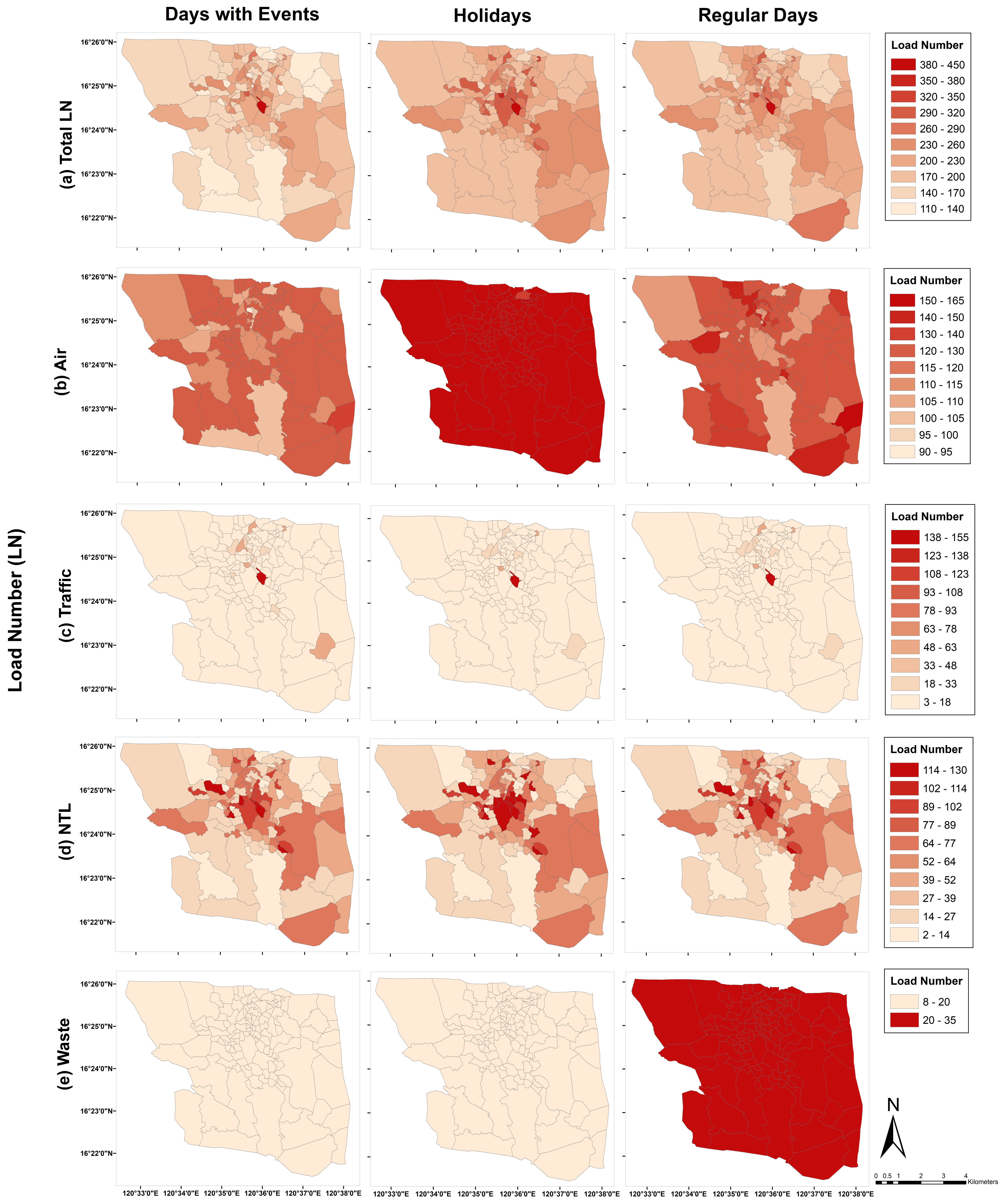
Sustainability, Free Full-Text

24-hour movement behaviour profiles and their transition in children aged 5.5 and 8 years – findings from a prospective cohort study, International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity
The Canadian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for Children and Youth encourage children and youth to “Sweat, Step, Sleep and Sit” the right amounts for a

Canadian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for Children and Youth (5-17): Tear Sheets

PDF) How do 24-h movement behaviours change during and after vacation? A cohort study

Canadian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for the Early Years released today — The Sandbox Project
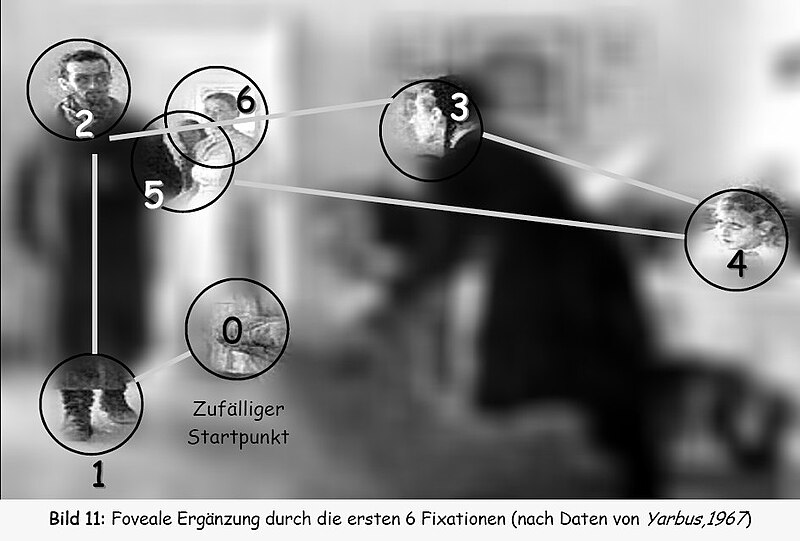
Eye movement - Wikipedia

Institución Vinculat on Instagram: Tomarse unas vacaciones es muy bueno para el cerebro, pero solo si lo haces bien 🏖️ 📌 Las vacaciones benefician la mente al ejercitar nuestro procesamiento sensorial y

Transtheoretical model - Wikipedia

Canadian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for the Early Years (0–4 years): An Integration of Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviour, and Sleep, BMC Public Health

A collaborative approach to adopting/adapting guidelines - The Australian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for the early years (Birth to 5 years): an integration of physical activity, sedentary behavior, and sleep







