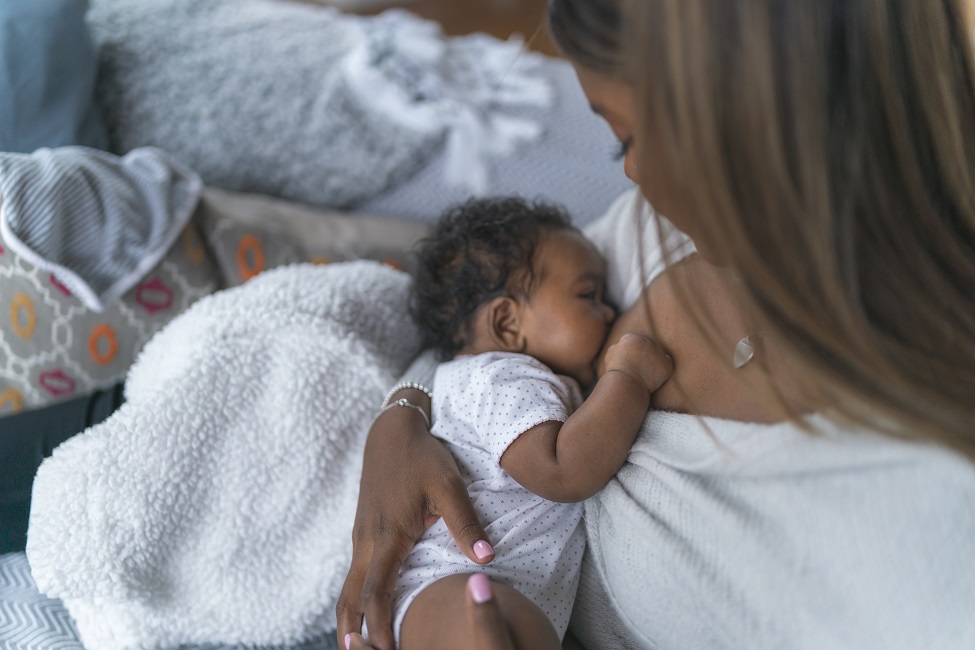
The Short Form of the Breastfeeding Self-Efficacy Scale as a Prognostic Factor of Exclusive Breastfeeding among Mandarin-Speaking Chinese Mothers - Wan-Yim Ip, Ling-Ling Gao, Kai-Chow Choi, Janita Pak-Chun Chau, Yang Xiao, 2016
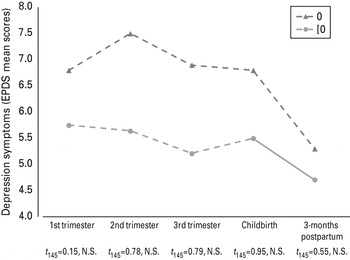
Breastfeeding is negatively affected by prenatal depression and reduces postpartum depression, Psychological Medicine

Celebrating National Breastfeeding Month: Nurturing Health and Bonding

ConsumerConnect Maternal Health: Breastfeeding may lower women's risk of postpartum depression ─Study
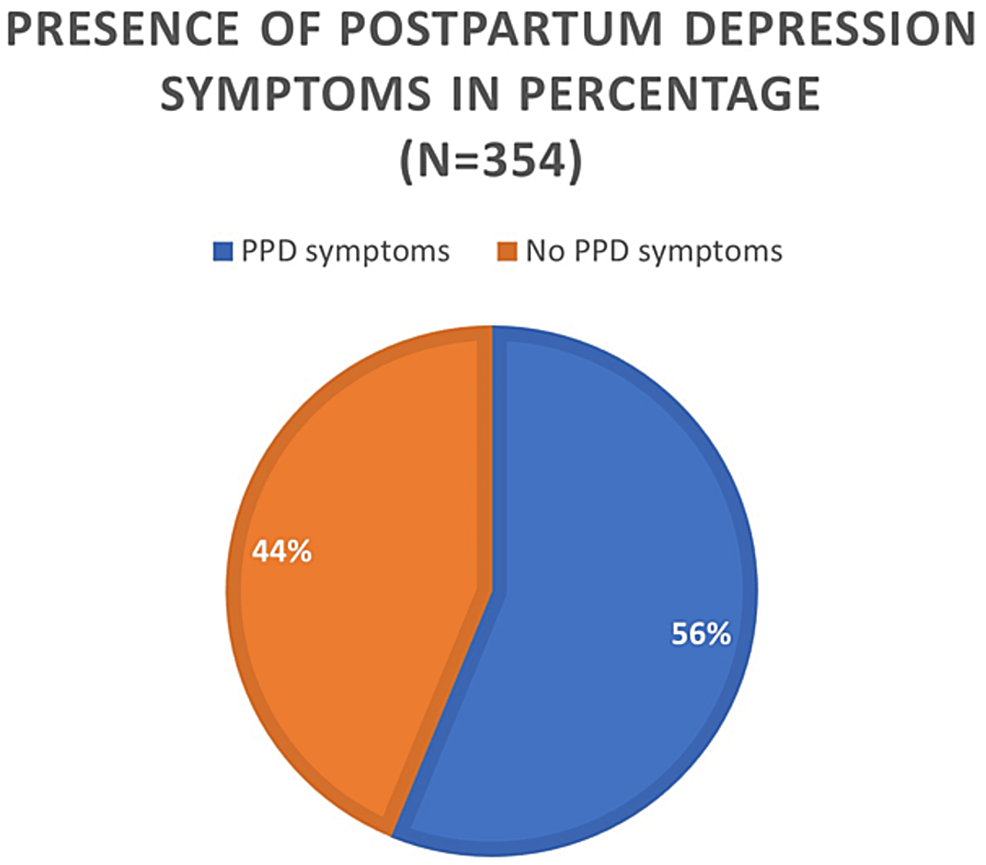
Cureus The Effect of Delivery Mode, ABO Blood Type, and Passive

Breastfeeding status and duration significantly impact postpartum depression risk
Cureus, Exploring the Efficacy of Ketamine as an Anesthetic and Antidepressant in Postpartum Depression: A Case Study Analysis
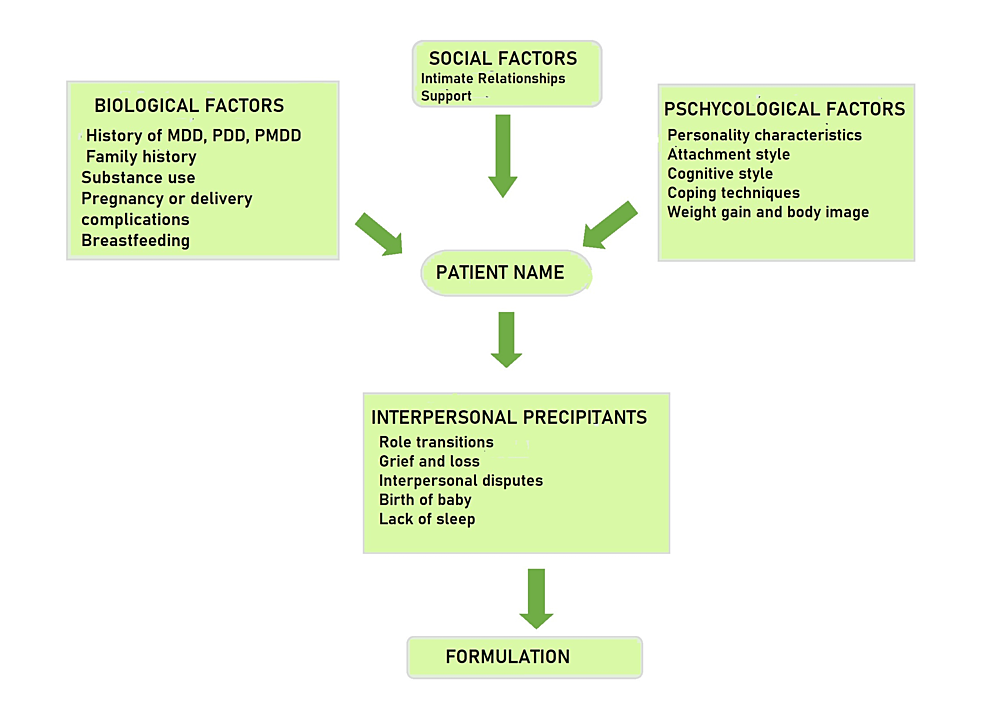
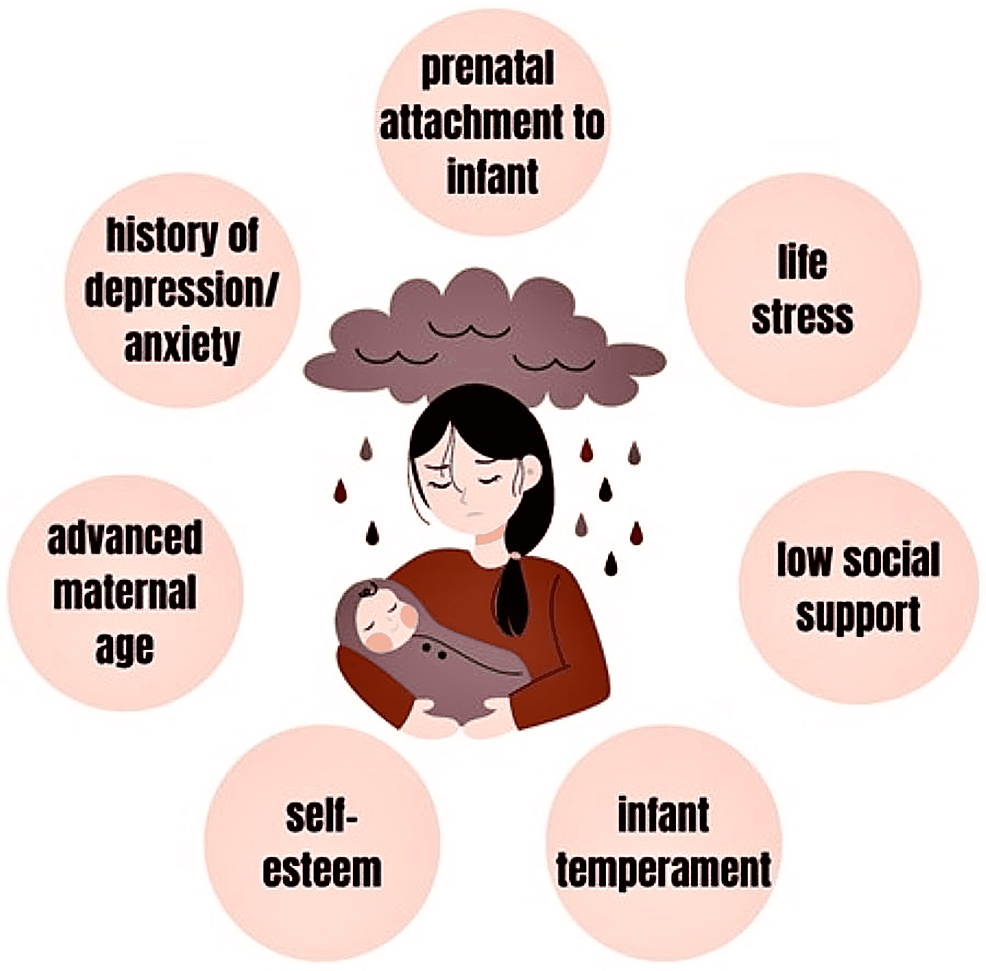
Cureus, A Review on Risk Factors of Postpartum Depression in India and Its Management
Association between postpartum depression level, social support level and breastfeeding attitude and breastfeeding self-efficacy in early postpartum women

Effectiveness of an integrated breastfeeding education program to
/medriva/media/post_banners/content/uploads/2024/01/benefits-of-breastfeeding-for-babies-and-mothers-20240119032036.jpg)
The Remarkable Benefits of Breastfeeding for Babies and Mothers
Depressed moms who breastfeed boost babies' m

Study protocol for the sheMATTERS study (iMproving cArdiovascular
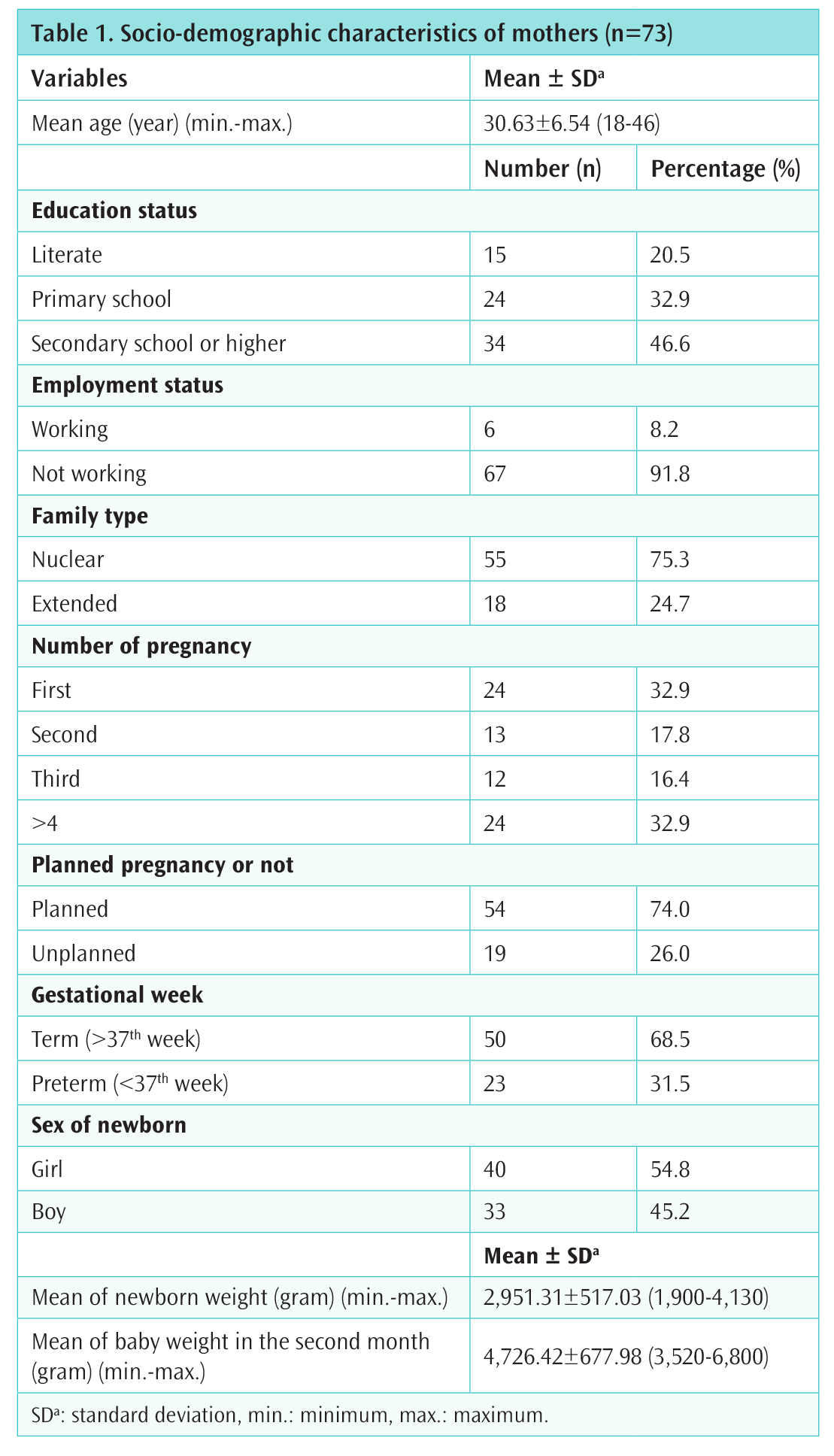
Cyprus Journal of Medical Sciences

Association between maternal postpartum depressive symptoms, socioeconomic factors, and birth outcomes with infant growth in South Africa