
Blood clots in veins and arteries can lead to heart attack, stroke, and pulmonary embolism, which are major causes of mortality. In the featured article of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine
Blood clots in veins and arteries can lead to heart attack, stroke, and pulmonary embolism, which are major causes of mortality. In the featured article of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine's (JNM) July 2017 issue, German researchers show that targeting GPIIb/IIIa receptors, the key receptor involved in platelet clumping, with a fluorine-18 (18F) labeled ligand is a promising approach for diagnostic imaging. Current imaging modalities rely on structural characteristics, such as vascular flow impairment, and do not address the critical molecular components.

New Single-Scan Method Could Detect Blood Clots Throughout the Body
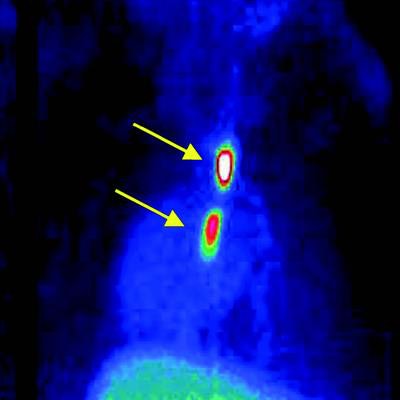
PET agent could advance blood clot imaging

Commentary to 18F-GP1, a Novel PET Tracer Designed for High-Sensitivity, Low-Background Detection of Thrombi: Imaging Activated Platelets in Clots—Are We Getting There? - Andrew W. Stephens, Norman Koglin, Ludger M. Dinkelborg, 2018
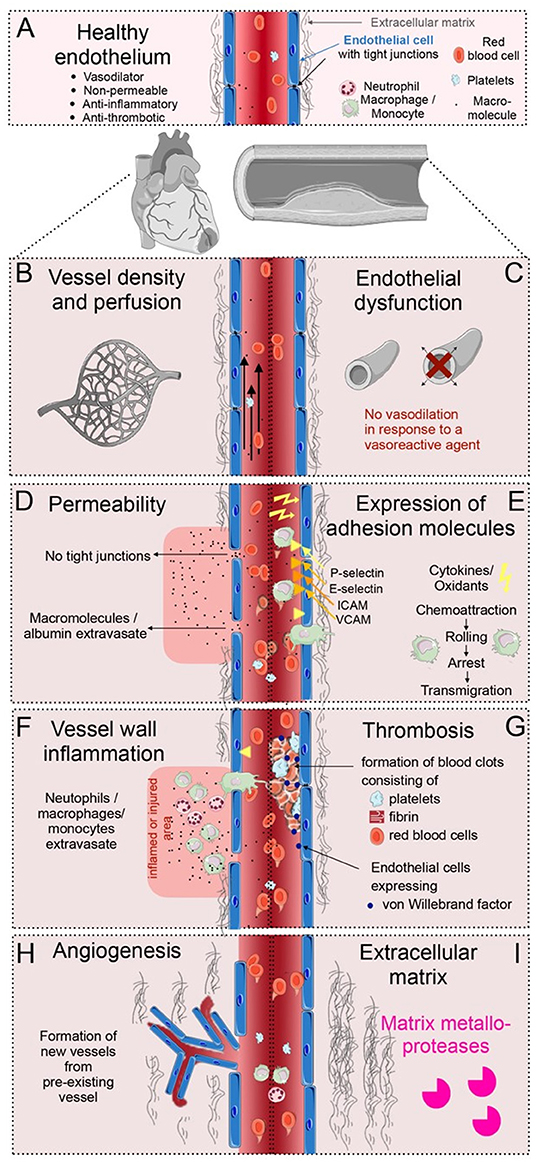
Frontiers Multi-Scale Imaging of Vascular Pathologies in Cardiovascular Disease

FDG–PET findings associated with various medical procedures and treatments
Cardiac PACS Integrates Advanced 2-D/3-D Echo Quantification Tools
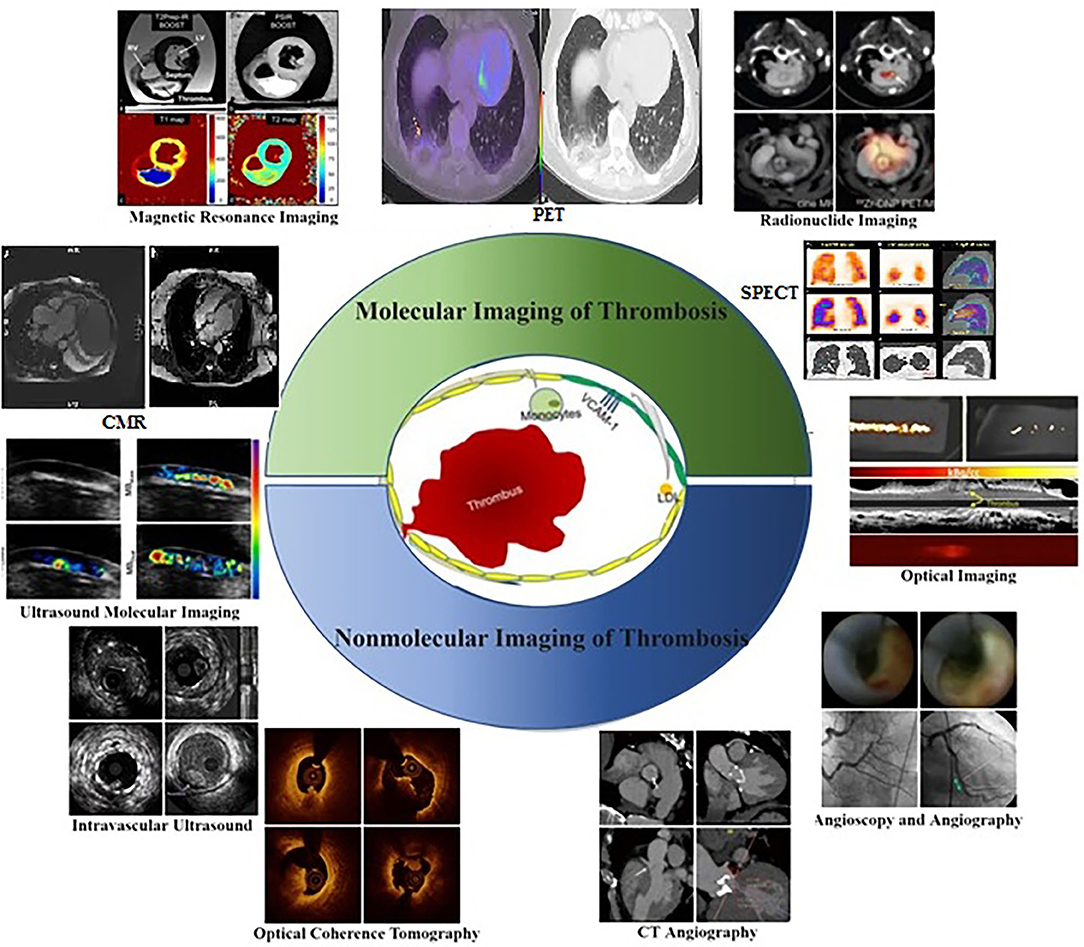
Frontiers Molecular Imaging and Non-molecular Imaging of Atherosclerotic Plaque Thrombosis
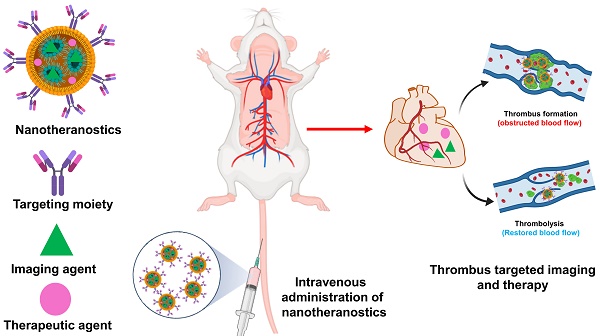
Nanoparticles for Thrombus Diagnosis and Therapy: Emerging Trends in Thrombus-theranostics
Study on Novel Cardiac PET Tracer Launches
PET/CT •

Rapid molecular imaging of active thrombi in vivo using aptamer-antidote probes - ScienceDirect

Characteristics of patients (n=26) with thrombosis identified on FDG-PET/CT

Manhattan Isotope Starts Formal Process to Produce Sr-82






