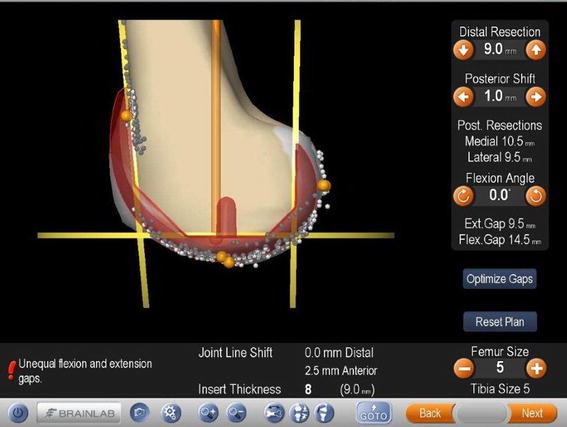
Download scientific diagram | Navigation image of the femoral component planning. The size of the component matches the individual model of this patient knee well. Femoral component is placed at 0° of flexion. Please notice that the flexion gap is 12 mm being 1.5 mm larger than the extension gap and hence showing unequal flexion and extension gaps. from publication: Intentional Femoral Component Flexion - A Method to Balance the Flexion-extension Gap in Navigated Total Knee Replacement | Introduction: Flexion of the femoral component has been described as a theoretical possibility to balance flexion and extension gap. Computer navigation has made it possible to intentionally flex the femoral component in a controlled fashion to take advantage of the | Knee, Navigation and Balance | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
Bioengineering, Free Full-Text
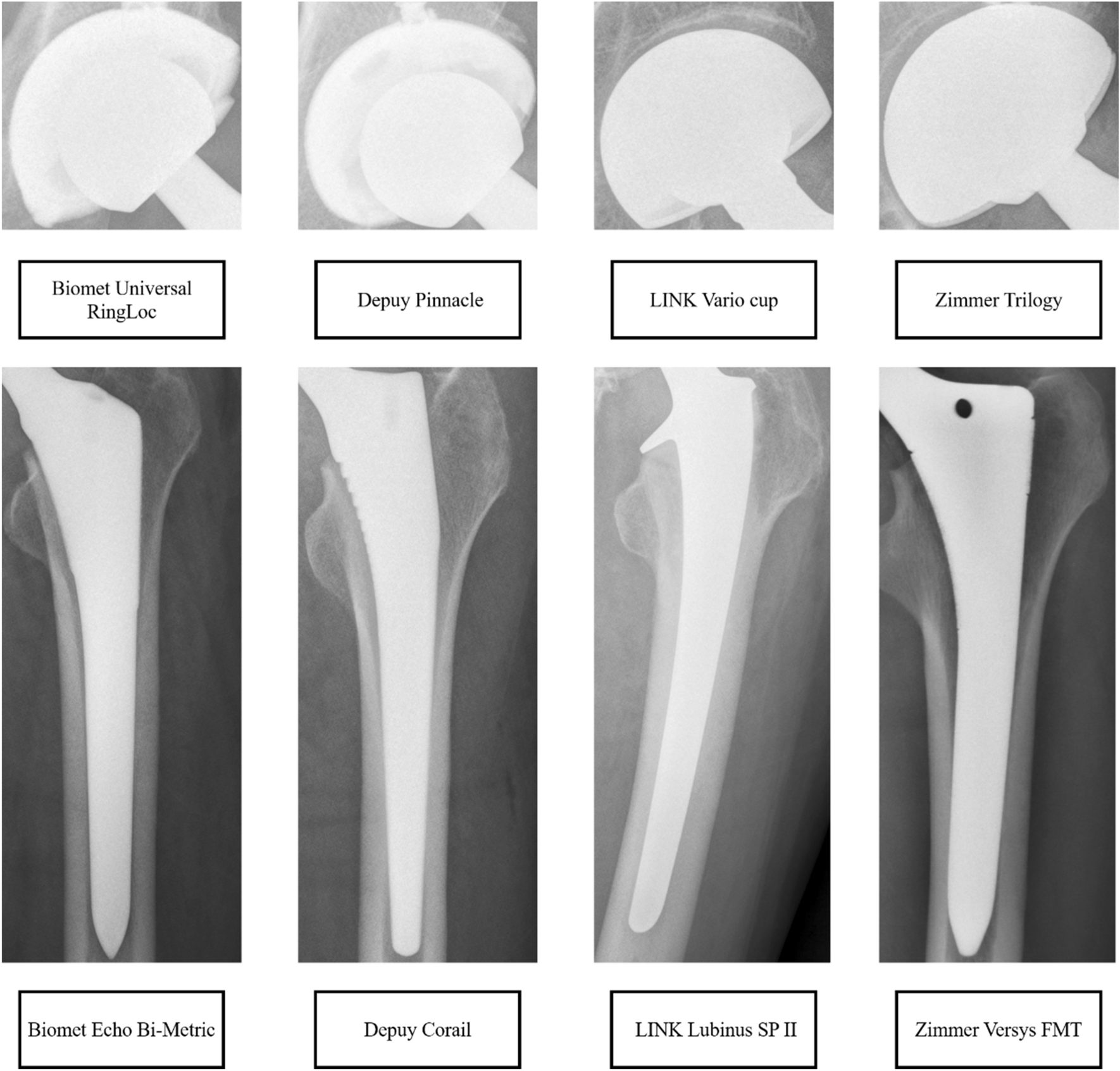
Automated identification of hip arthroplasty implants using artificial intelligence

Technological Aids in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Navigation, Patient-Specific Instrumentation, and Robotics

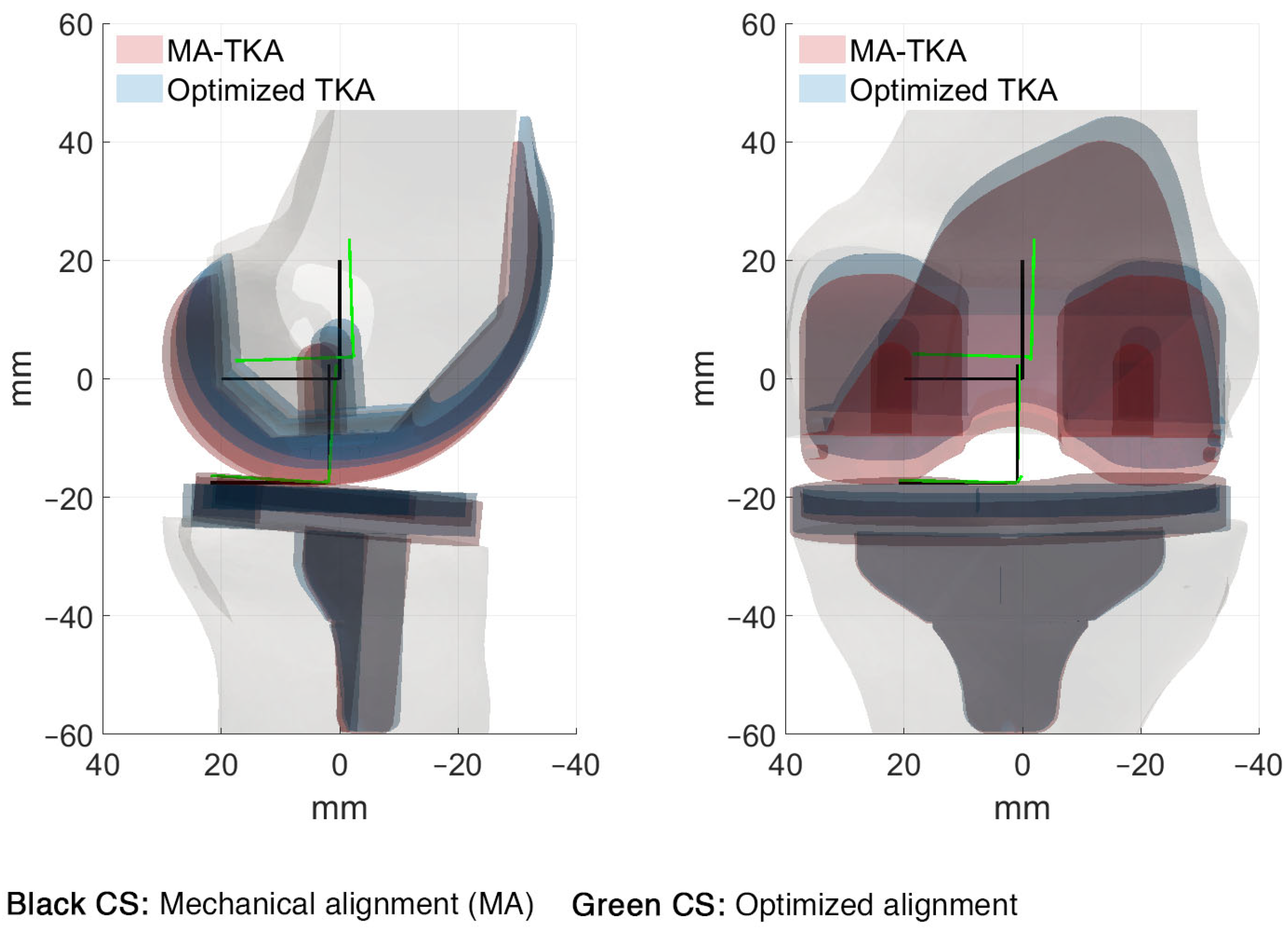
Computer-based analysis of different component positions and insert thicknesses on tibio-femoral and patello-femoral joint dynamics after cruciate-retaining total knee replacement - ScienceDirect
Inaccurate offset restoration in total hip arthroplasty results in reduced range of motion
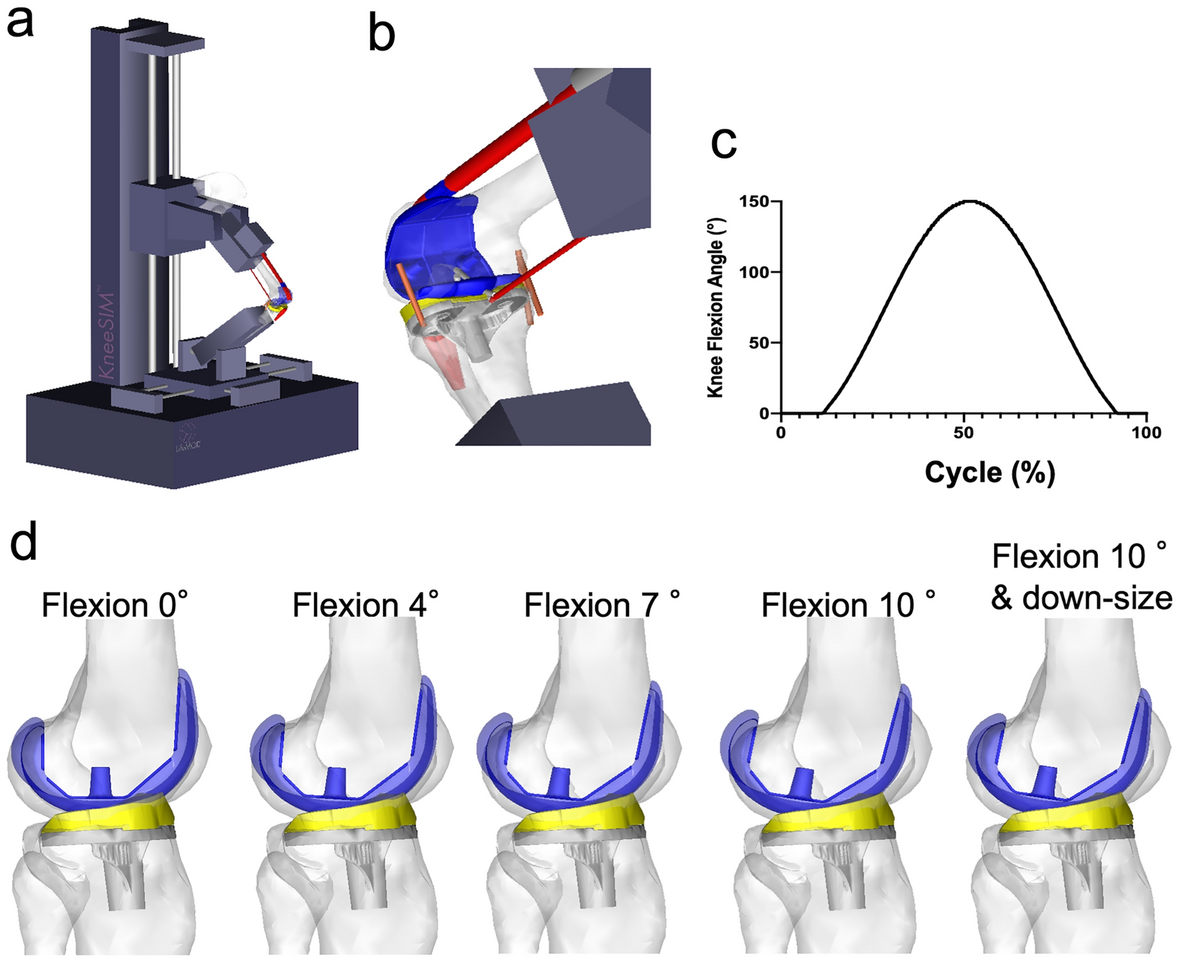
Excessive flexed position of the femoral component causes abnormal
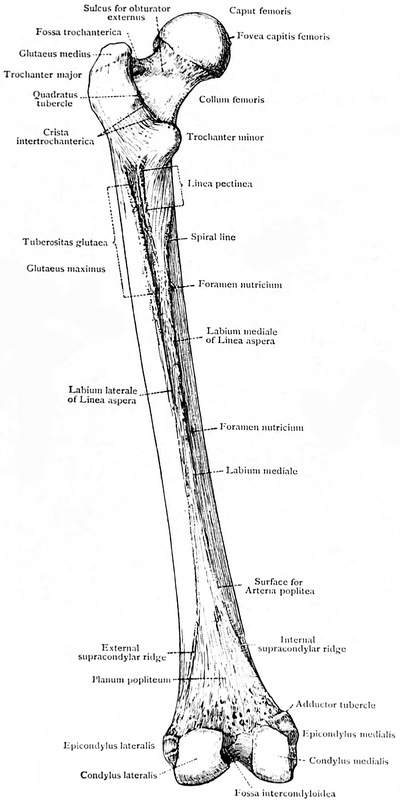
Femur - Physiopedia

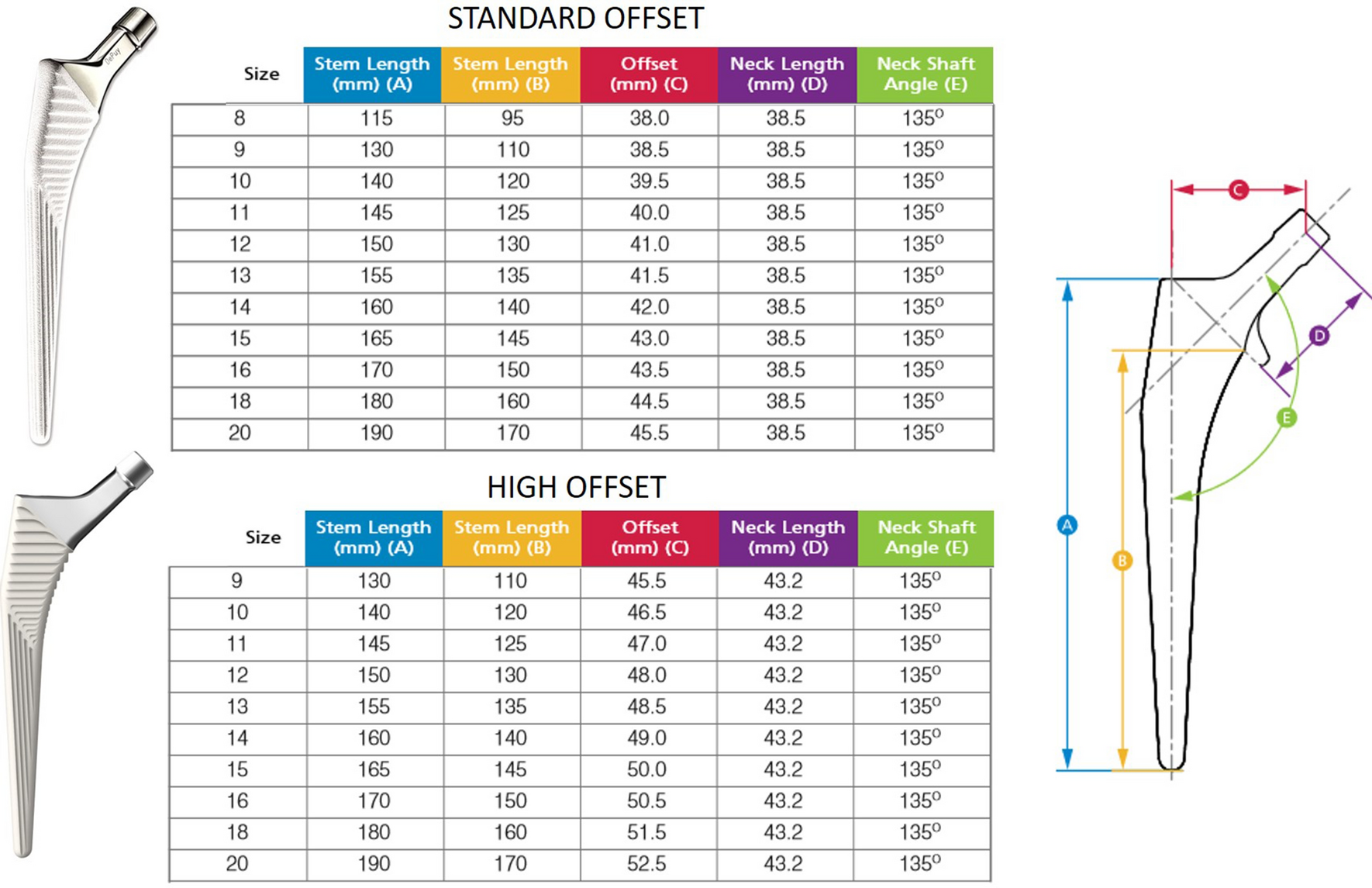
Femoral stem and acetabular shell templating.

Schematic shows that flexing the femoral component 5° and 10° reduces

Referencing the center of the femoral head during robotic or computer-navigated primary total knee arthroplasty results in less femoral component flexion than the traditional intramedullary axis - ScienceDirect
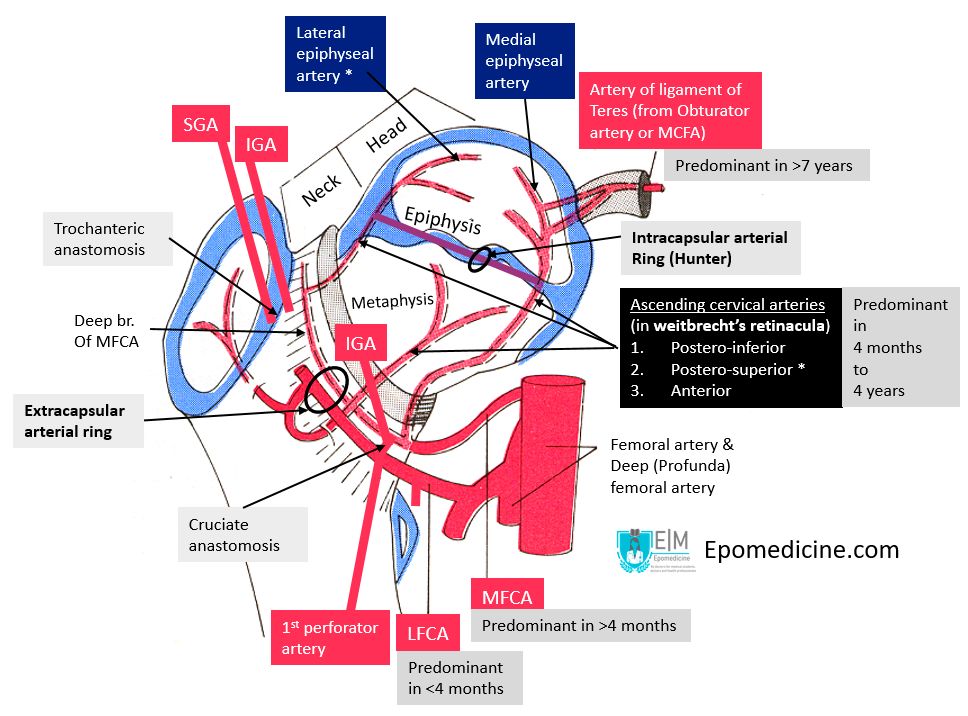
Blood supply of femoral head

Femoral planning screen for piKA (a) and pGB (b). Femoral component

Three-dimensional measurements on the postoperative femur. Definitions
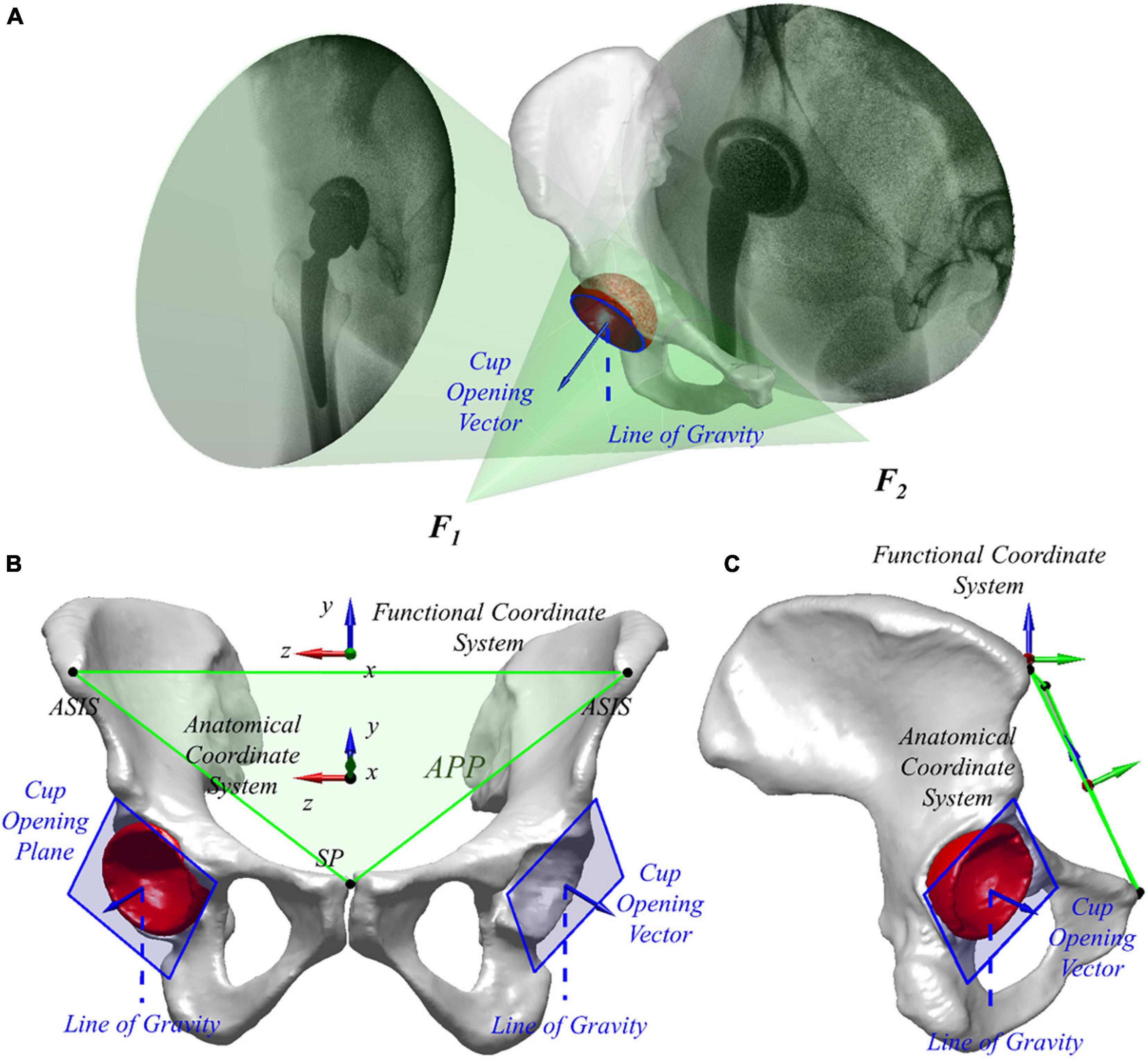
Frontiers Well-Placed Acetabular Component Oriented Outside the Safe Zone During Weight-Bearing Daily Activities
Comparison between two- and three-dimensional methods for offset measurements after total hip arthroplasty