ABSTRACT The global prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is increasing. T2DM is more common in patients with psychiatric disorders and those who take certain psychotropic drugs. T2DM occurs in 2%–7% of women of reproductive age. The prevalence of pregestational diabetes is 0.5%–2.4%, and that of gestational diabetes is 7%–28%, depending on geographical region. About 20%–50% of pregnancies, across the world, are unplanned; this figure is higher, at about 65%, in women with psychiatric disorders. As a result, many women of reproductive age who have diabetes, including women who do not know that they have diabetes, may unintentionally become pregnant, thus unknowingly exposing their pregnancy to diabetes and its treatment. Exposure of pregnancy to pregestational and gestational diabetes is associated with risks to the mother as well as risks to the child. Risks to the mother include obesity, hypertension, and preeclampsia. Risks to the child include spontaneous abortion, fetal death, macrosomia, major congenital malformations (MCMs), preterm delivery, neonatal hypoglycemia, neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, and neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. A recent large retrospective cohort study with data from 6 countries in Europe, Asia, and North America found that, in about 51,000 women with pregestational T2DM, neither MCMs nor cardiac malformations were more prevalent in offspring of children periconceptionally exposed to second-line antidiabetic treatments relative to exposure to insulin. These findings are reassuring but have limitations that are discussed. A reasonable conclusion from a reading of the reviewed literature is that pregestational and gestational diabetes are best treated during pregnancy, that insulin is a first-line treatment, that metformin is an increasingly accepted alternative, and that safety data on second-line antidiabetic treatments are, so far, reassuring. J Clin Psychiatry 2024;85(1):24f15318 Author affiliations appear at the end of this article

A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diabetes During Pregnancy

Childhood Adversity and Schizophrenia: The Protective Role of Resilience in Mental and Physical Health and Metabolic Markers
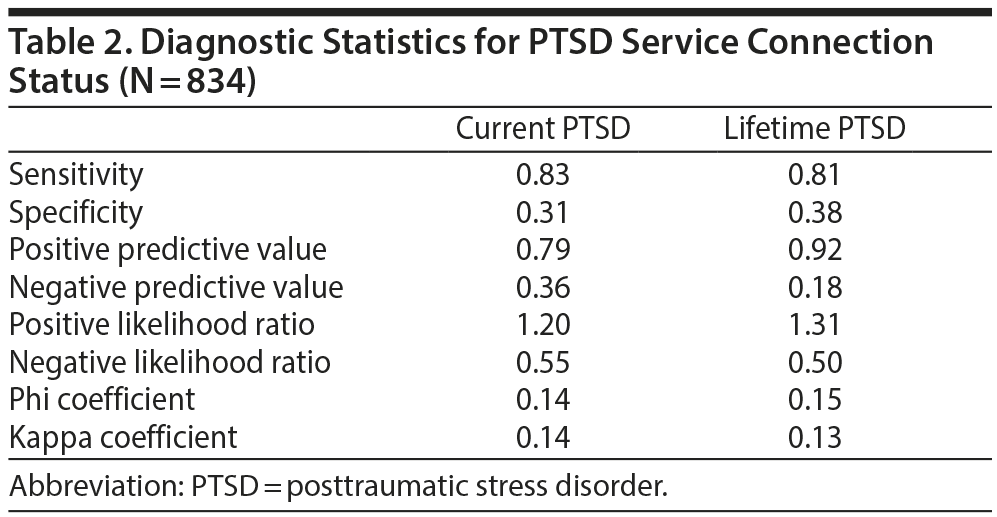
Validity of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Service Connection Status in Veterans Affairs Electronic Records of Iraq and Afghanistan Veterans
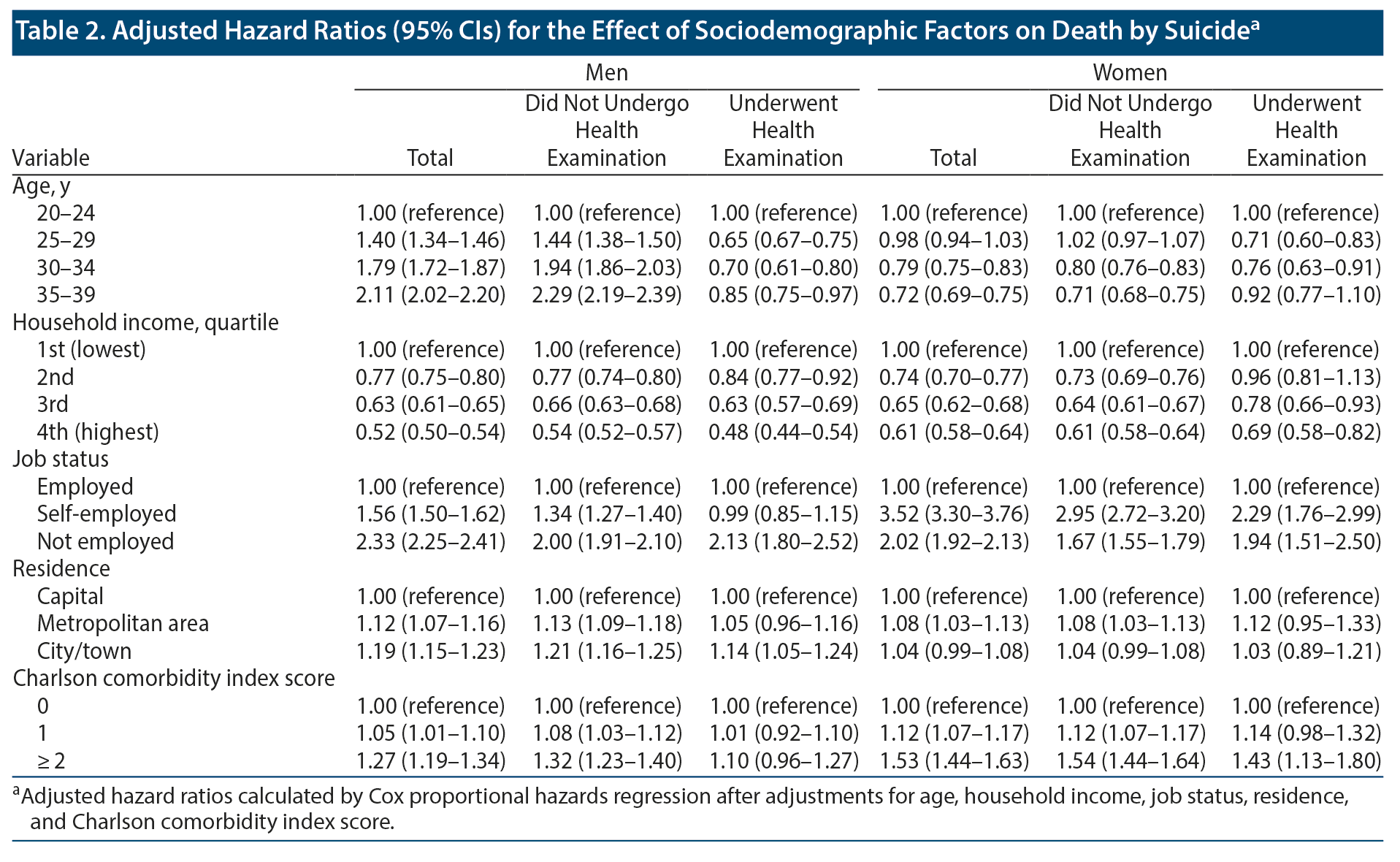
Sociodemographic Factors, Health Behaviors, and Biological Indicators Associated With Suicide Mortality Among Young Adults in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study Among 15 Million Men and Women

A Comparison of Glyburide and Insulin in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
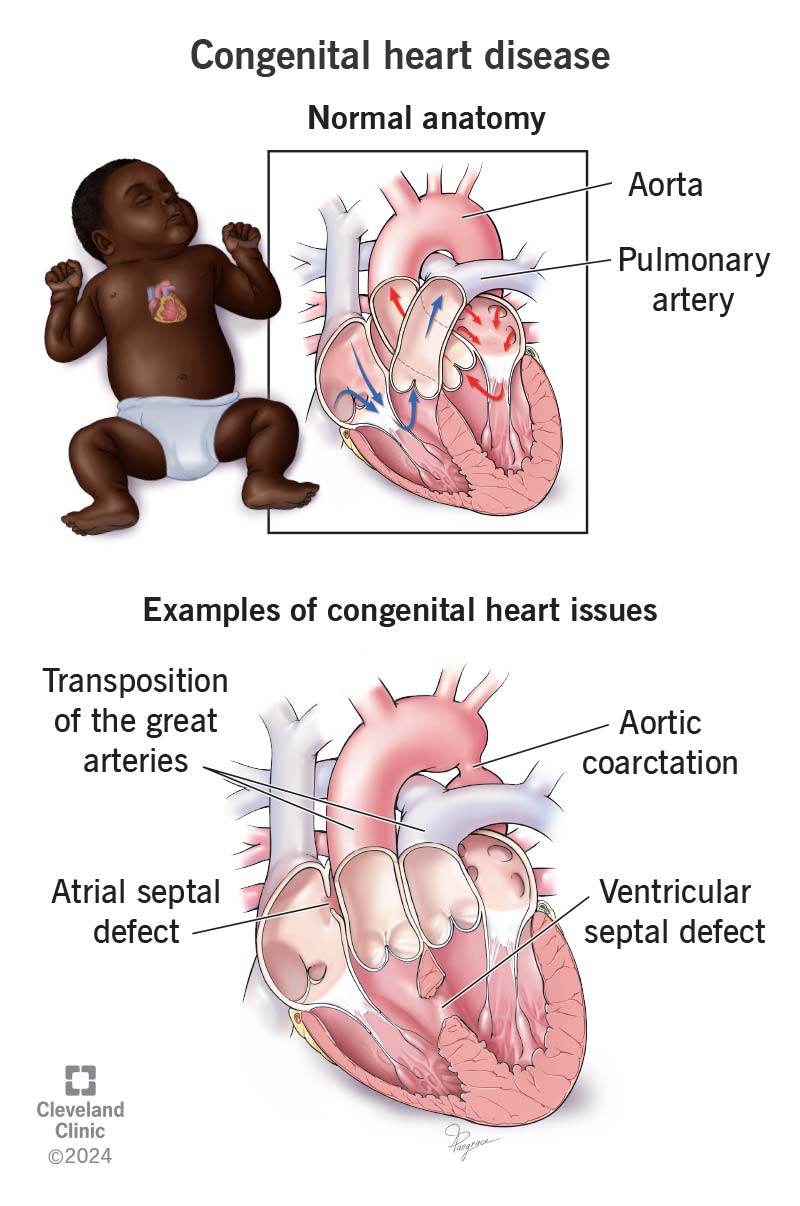
Congenital Heart Disease: Symptoms & Treatment

PDF) Congenital Malformations Associated with Maternal Diabetes

Sonia Grandi, PhD on X: 🚨Looking for patients with lived

Diabetes drug linked to genital birth defects in baby boys

A Review on Homoeopathic Medicines in Diabetes Mellitus by
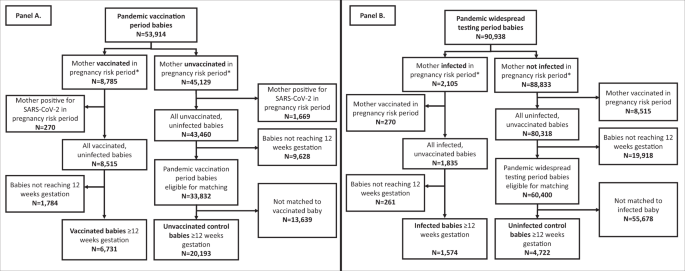
A population-based matched cohort study of major congenital

The Implication of Combat Stress and PTSD Trajectories in Metabolic Syndrome and Elevated C-Reactive Protein Levels: A Longitudinal Study
Men's use of diabetes drug just before conception is linked to a
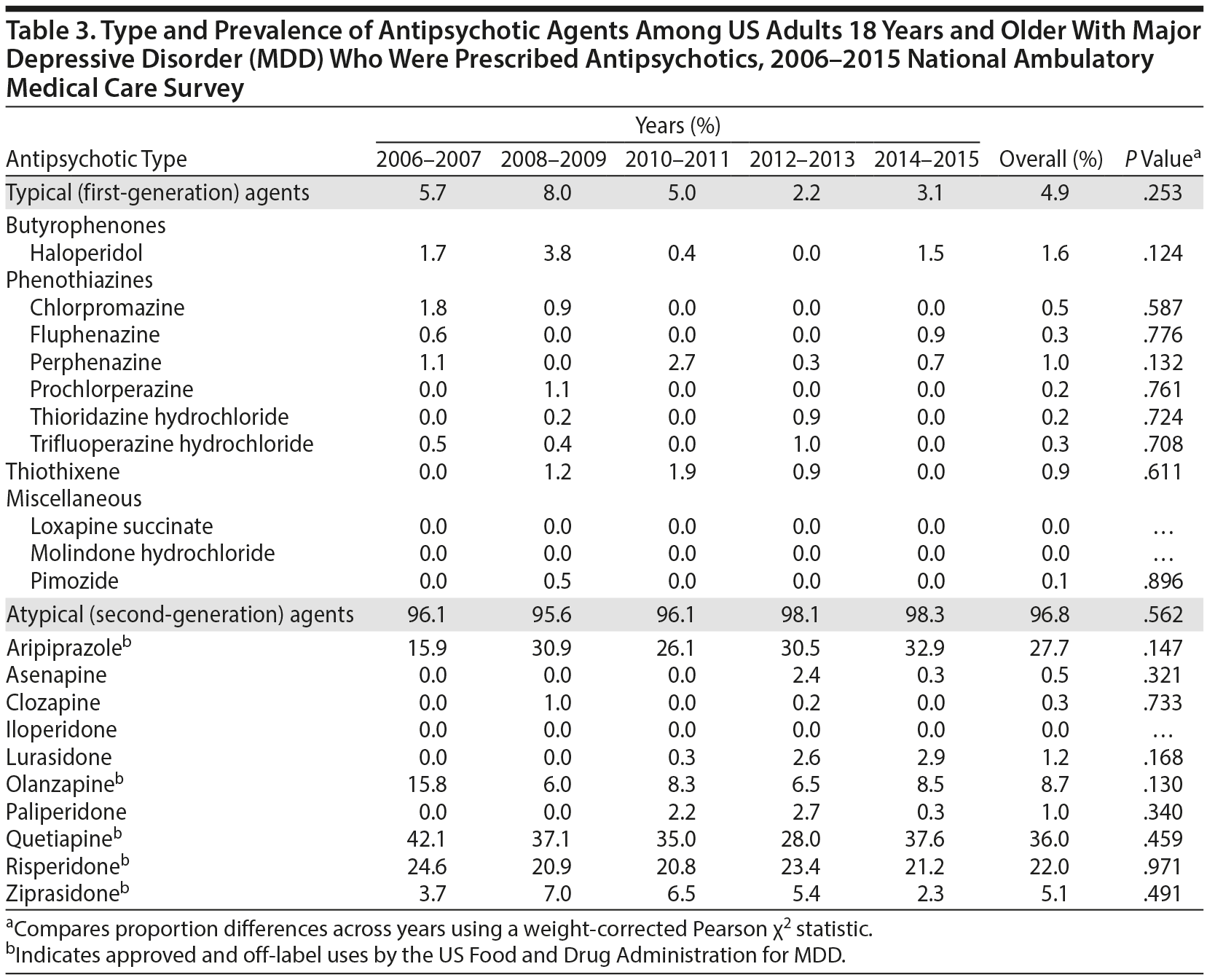
Antipsychotic Prescriptions Among Adults With Major Depressive Disorder in Office-Based Outpatient Settings: National Trends From 2006 to 2015







