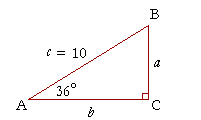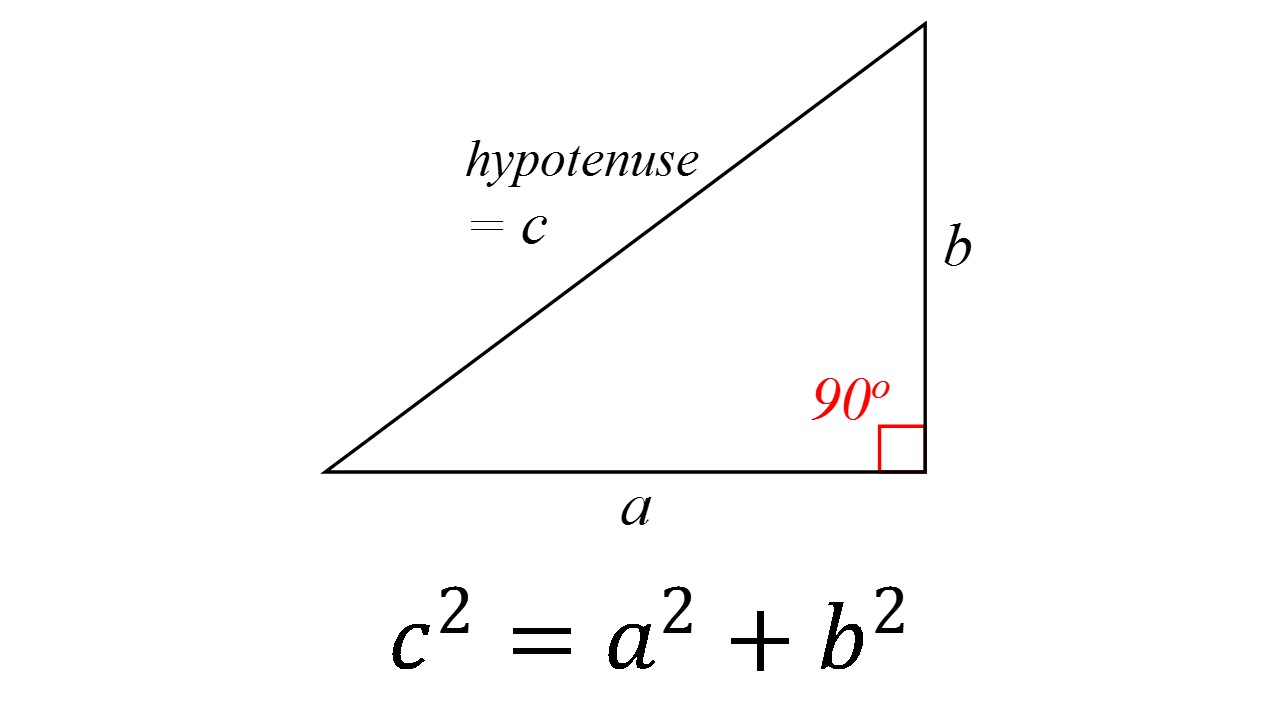
c^2 != a^2 + b^2, therefore, this cannot be a right triangle. The Pythagorean Theorem applies to right angle triangles, where the sides a and b are those which intersect at right angle. The third side, the hypotenuse, is then c To test whether the given lengths of sides create a right triangle, we need to substitute them into the Pythagorean Theorem - if it works out then it is a right angle triangle: c^2 = a^2 + b^2 15^2 != 5^2+10^2 225 != 25+100 225 != 125 In reality, if a=5 and b=10 then c would have to be c^2 = 125 c =sqrt(125) = 5sqrt(5)~= 11.2 which is smaller than the proposed value in the question. Therefore, this cannot be a right triangle.
What is the equation for the Pythagorean theorem, and how is it

How do you use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the

Answered: Is the following shape a right…

Determine whether the law of sines or the law of cosines is needed
How to Calculate the Sides and Angles of Triangles Using
What is the Pythagorean theorem, and how is it used to solve
Pythagoras' theorem - BBC Bitesize
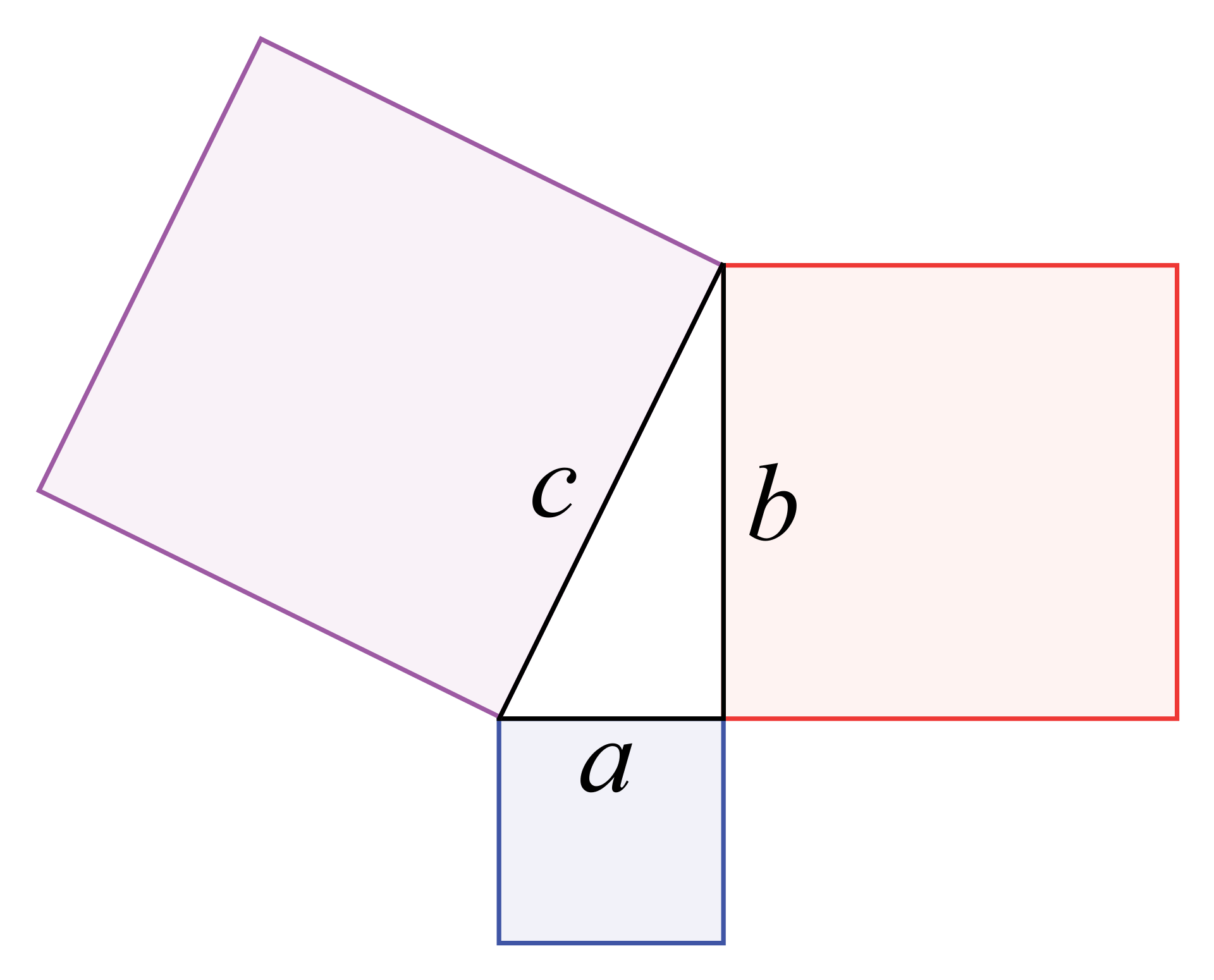
The Pythagorean Theorem - Trigonometry

If LaTeX: a^2+b^2=c^2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 , then it is a right
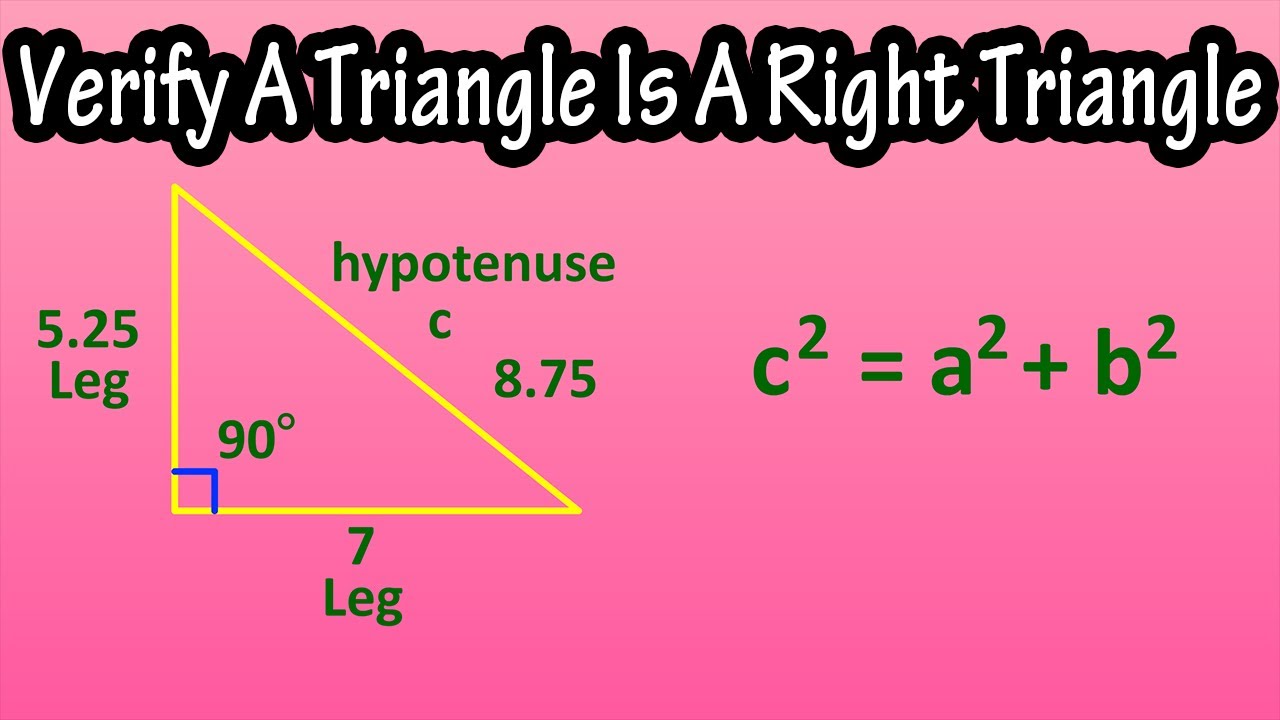
How To Verify A Triangle Is A Right Triangle Using The Pythagorean
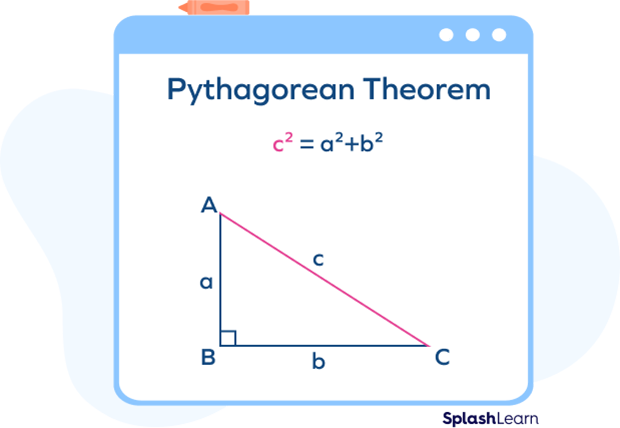
Pythagorean Triples - Definition, Formula, Examples, Facts
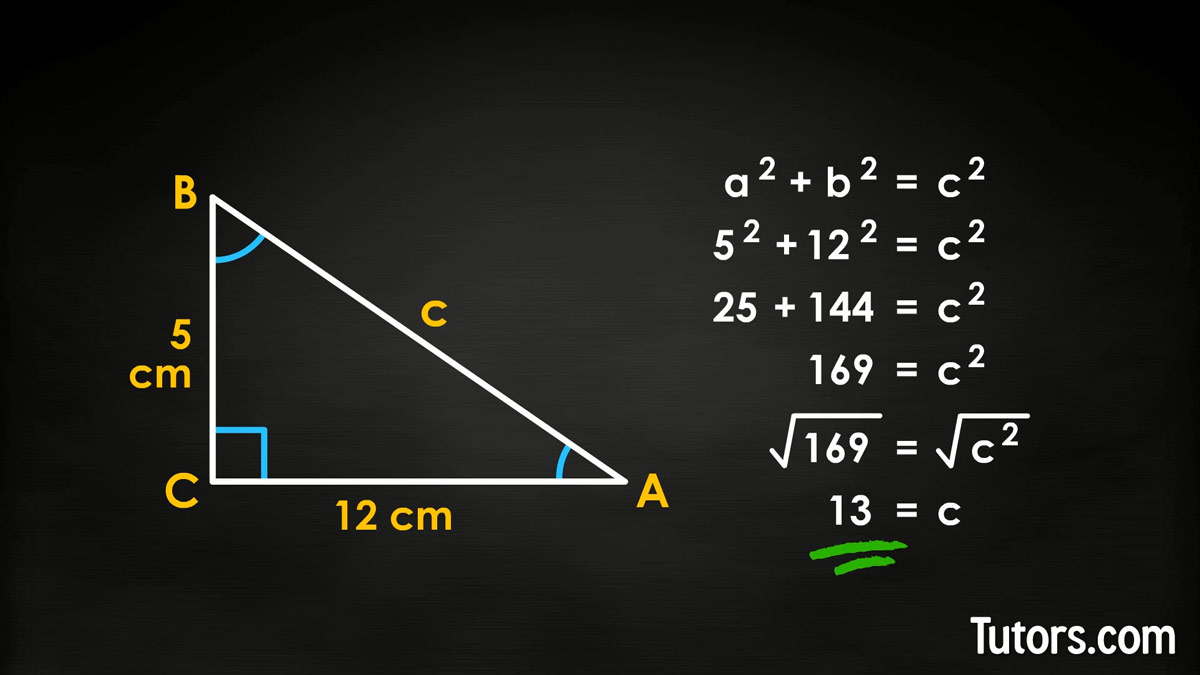
Pythagorean Theorem [Video] Formula, Definition, Examples & Proof
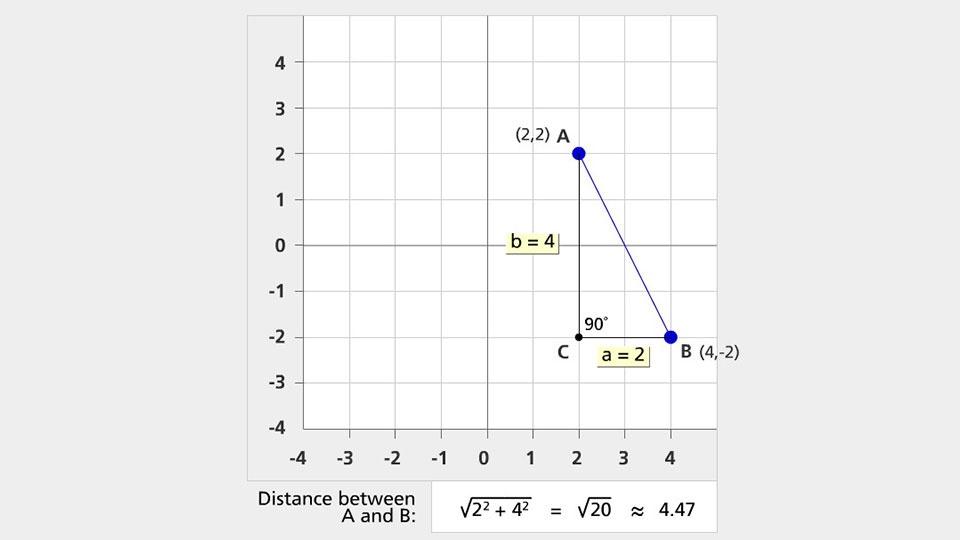
Calculating Distance Using the Pythagorean Theorem